Typhoid fever is a bacterial infection caused by the bacterium Salmonella typhi. It is a serious illness that can be life-threatening if left untreated. Typhoid fever is typically transmitted through contaminated food and water or through direct contact with an infected person’s feces.
The main cause of typhoid fever is infection with the bacterium Salmonella typhi. This bacterium is primarily found in the feces and urine of infected individuals and can be spread through contaminated food, water, or close contact with infected individuals.
The bacterium can contaminate food and water sources through poor sanitation and hygiene practices, including improper disposal of human waste and improper hand-washing after using the toilet. In some cases, the bacterium can also be spread through contact with contaminated surfaces, such as doorknobs, countertops, or other objects.
We're now on WhatsApp. Click here to join.
Risk factors for typhoid fever include traveling to areas where the disease is common, such as parts of Asia, Africa, and South America. Additionally, individuals who work in healthcare, sanitation, or food service may be at increased risk of exposure to the bacterium.
It is important to note that not all individuals who are exposed to the bacterium will develop typhoid fever. Some individuals may become asymptomatic carriers of the bacterium, meaning they are able to spread the infection to others even though they do not exhibit symptoms of the disease themselves.
How Do People Get Typhoid Fever?
Typhoid fever can be contracted through contaminated food or water, as well as through close contact with infected individuals. The bacterium Salmonella typhi can be present in the feces, urine, or vomit of infected individuals and can contaminate surfaces or objects. Practicing good hygiene, avoiding untrusted sources of food and water, and getting vaccinated can help reduce the risk of infection. Casual contact is not a major risk factor for the disease.
Does typhoid spread by kissing?
No, typhoid doesn’t spread by kissing. You usually don’t get typhoid fever directly from another person. But you can get it if you touch something they’ve touched if they don’t wash their hands after going to the bathroom.
How Is Typhoid Fever Diagnosed?
Typhoid fever can be diagnosed through a combination of clinical evaluation, laboratory tests, and imaging studies. The diagnosis of typhoid fever can be challenging because the early symptoms of the disease can be non-specific and similar to other common illnesses, such as the flu or gastroenteritis.
Here are some of the common methods used to diagnose typhoid fever:
- Blood tests: Blood tests are the most common diagnostic method for typhoid fever. Blood samples are collected from the patient and analyzed for the presence of antibodies against Salmonella typhi. These antibodies are produced by the body in response to the infection and can be detected by a laboratory test.
- Stool culture: A stool culture is a test in which a small sample of stool is collected from the patient and analyzed for the presence of Salmonella typhi bacteria. This test is especially useful in detecting carriers of the bacteria who are not showing any symptoms of the disease.
- Urine culture: A urine culture is a test in which a small sample of urine is collected from the patient and analyzed for the presence of Salmonella typhi bacteria. This test can be useful in detecting carriers of the bacteria who are not showing any symptoms of the disease.
- Imaging studies: Imaging studies such as X-rays or ultrasounds may be used to detect complications of typhoid fever, such as intestinal bleeding or perforation.
It is important to note that laboratory tests alone may not be enough to confirm a diagnosis of typhoid fever, and clinical evaluation by a healthcare provider is necessary to determine the appropriate course of treatment.
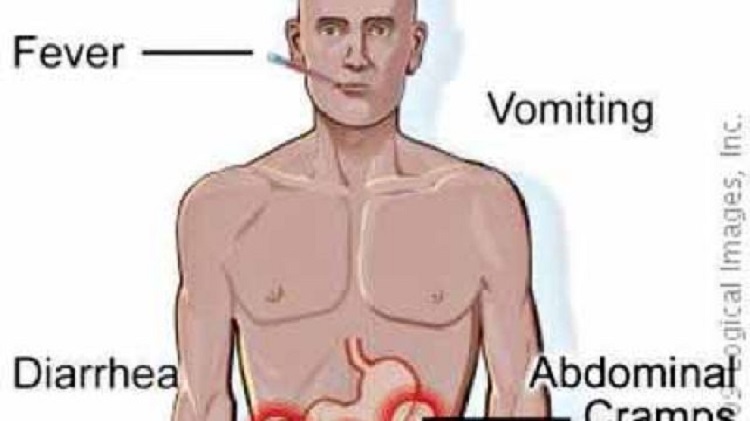
Symptoms Of Typhoid Fever
The symptoms of typhoid fever can vary in severity and can develop gradually over the course of several days to weeks after infection with the bacterium Salmonella typhi. Some common symptoms of typhoid fever include:
- High fever (often over 103°F or 39.5°C)
- Weakness and fatigue
- Abdominal pain and discomfort
- Headache
- Loss of appetite
- Diarrhea or constipation
- Rash of flat, rose-colored spots
- Cough
- Enlarged spleen and liver
- Delirium or confusion (in severe cases)
Symptoms can be mild or severe, and can last for several weeks. Some individuals may develop complications, such as intestinal bleeding or perforation, which can be life-threatening if not treated promptly. If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention right away.
Treatment Of Typhoid Fever
Typhoid fever is a bacterial infection caused by Salmonella typhi. It is treated with antibiotics and supportive care. The treatment options include:
- Antibiotics: Antibiotics are the mainstay of treatment for typhoid fever. Commonly used antibiotics include ciprofloxacin, azithromycin, and ceftriaxone. Your doctor will prescribe an appropriate antibiotic based on your age, medical history, and severity of the infection.
- Supportive care: It is important to stay hydrated during the course of the illness. Drinking plenty of fluids, including water, fruit juices, and electrolyte solutions can help to prevent dehydration. In severe cases, intravenous fluids may be necessary.
- Rest: Getting enough rest is important to help your body fight the infection. It is recommended that you take a break from work or school until you have fully recovered.
- Surgery: In rare cases, surgery may be necessary if complications such as intestinal perforation or abscess formation occur.
It is important to complete the full course of antibiotics prescribed by your doctor, even if you start feeling better before the medication is finished. This will help to prevent the development of antibiotic resistance and reduce the risk of relapse.
Complications of typhoid
Typhoid fever can lead to various complications, especially if it is not treated properly or if treatment is delayed. Some of the possible complications of typhoid fever include:
- Intestinal bleeding: Typhoid fever can cause inflammation and ulceration in the intestines, which can lead to bleeding.
- Perforation of the intestines: In severe cases, the ulceration caused by typhoid fever can lead to a hole or perforation in the intestines. This can cause abdominal pain, fever, and sepsis.
- Encephalopathy: Typhoid fever can affect the brain and cause encephalopathy, a condition characterized by confusion, agitation, and seizures.
- Pneumonia: Typhoid fever can lead to pneumonia, a serious lung infection that can cause difficulty breathing and other respiratory symptoms.
- Hepatitis: Typhoid fever can cause inflammation of the liver, leading to hepatitis.
- Kidney failure: In rare cases, typhoid fever can cause kidney failure, which can lead to serious complications.
- Other complications: Typhoid fever can also lead to other complications such as myocarditis (inflammation of the heart muscle), arthritis (joint inflammation), and osteomyelitis (bone infection).
It is important to seek medical attention if you suspect that you have typhoid fever, especially if you experience any of the above complications or symptoms that are not improving with treatment. Early diagnosis and prompt treatment can help to prevent complications and improve outcomes.
Read Latest Health News Here Or Even On Flexhealthtips.com